Introduction
Diamond and CBN are defined as super hard materials because of their extremely hardness that surpasses the traditional abrasive materials such as aluminum oxide (Al2O3) or silicon carbide (SiC).
Diamond and CBN wheels are widely used in high effective grinding processes and offer substantially benefits over traditional wheels. The main advantages of diamond and CBN tools:
• very long tool life and profile stability;
• short grinding times;
• short handling times;
• lack of thermal damage to the workpiece;
• ensure appropriate workpiece quality.
In respect of diamond's chemical affinity to iron, diamond tools do not compete with CBN tools but mutually supplement the range of their applications.
Diamond application
Diamond is the hardest abrasive material in the world known to man. Its hardness, wear and thermal resistance make the diamond the most appropriate abrasive to machining such materials as:
• cemented carbides, cermets;
• glass and ceramics;
• silicon, graphite, quartz;
• fibber, reinforced plastics;
• natural stone;
• other hard-to-machine materials (PCD, PCBN).
CBN application
CBN is produced similarly to the diamond by high pressure and high temperature synthesis. CBN is the second the hardest man-made material, only surpassed by the diamond. Thanks to their chemical features and considerable lower wear, CBN tools are used for grinding such hard-to-process steel as:
• hardened high speed steel (HSS);
• chrome steel;
• bearing steel;
• stainless steel with hardness >55HRC;
• stellited steels.
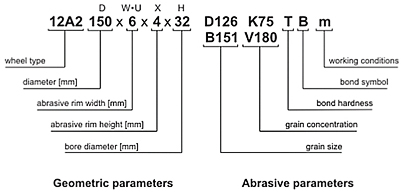
Wheel designation scheme
Diamond and CBN resin bonded grinding wheels are designated according to the following scheme: